前言
异步行为是 JavaScript 的基础,但以前的实现不理想。在早期的 JavaScript 中,只支持定义回调函数来表明异步操作完成。串联多个异步操作是一个常见的问题,通常需要深度嵌套的回调函数(俗称 “地狱回调” )来解决。
为了解决地狱回调这个问题,ES6 根据 Promises/A+ 规范,实现了一个 Promise ,可以将异步行为以同步行为的流程表达出来。
ES6 从2015发布到现在,其中 Promise 已经在开发中到处使用,或许在3年前的中高级前端面试中会问 Promise 的概念和用法,现在一般都会叫你实现一个 Promise,这样不仅考察了你对 Promise 的概念和用法的掌握程度,也考察了你对 ES6 中语法及其应用的掌握程度。
想要实现一个 Promise,就要遵循 Promise/A+ 规范,业界所有 Promise 的类库都遵循这个规范。当然规范也是根据业务场景一点点完善的,本专栏从业务场景入手,带你一步一步实现一个 Promise ,比较规范不好记忆,业务场景做多了还不好记忆吗。
希望通过本专栏给你在中高级前端的面试中增加点底气。
一、分析 Promise 的业务场景
先来简单分析一下 Promise 的业务场景。
- Promise 中有三个状态 Pending(进行中)、Fulfilled(已成功)、Rejected(已失败)。外界无法改变这个三个状态,而且一旦状态改变就不会再变。
-
实例化一个 Promise 需要传入一个
executor函数 ,业务代码在executor函数中执行,另外executor函数接收两个参数resolve和reject。resolve和reject是 Promise 构造函数的内置函数。new Promise((resolve, reject) =>{ //... 业务代码 }) -
在
executor函数中业务代码执行成功了,调用resolve函数,把 Promise 的状态变为已成功,另外通过参数把业务代码的执行成功的结果传递到 Promise 中。 -
在
executor函数中业务代码执行失败了,调用resolve函数,把 Promise 的状态变为已失败,另外通过参数把业务代码的执行失败的原因传递到 Promise 中。 -
实例方法
then的第一个参数是业务代码执行成功的回调函数,第二个参数是业务代码执行失败的回调函数,当业务代码执行完毕后,会根据执行结果调用对应的回调函数,且这些回调函数接收业务代码的执行结果作为参数。 -
通过实例方法
catch来添加业务代码执行失败的回调函数。
下面就一一来实现 Promise 的功能。
二、初步搭建 Promise 的构造函数
按照上面对 Promise 的业务场景分析,Promise 的构造函数应该有这些内容:
-
Promise 是个类,在 ES6 中用 Class 语法创建。
-
Promise 构造函数接收
executor函数作为参数,且在其中执行executor函数。 -
Promise 构造函数中有
resolve和reject内置方法,并作为参数传递给executor函数。 -
设置个实例属性
status来存储状态。 -
内置函数
resolve可以把状态变为已成功,内置函数reject可以把状态变为已失败,且一旦状态改变就不会再变。
另外在构造器外面用 Symbol 来创建三个状态 Pending(进行中)、Fulfilled(已成功)、Rejected(已失败)。
// 用Symbol定义三种状态,防止外界改变状态。
const Pending = Symbol('Pending'); // 进行中
const Fulfilled = Symbol('Fulfilled'); // 已成功
const Rejected = Symbol('Rejected'); // 已失败
class Promise {
constructor(executor){
this.status = Pending;//存储 Promise 的状态
const resolve = () =>{
// 只有当状态为 Pending 才会改变,来保证一旦状态改变就不会再变。
if(this.status === Pending){
this.status = Fulfilled;
}
};
const reject = () =>{
// 只有当状态为 Pending 才会改变,来保证一旦状态改变就不会再变。
if(this.status === Pending){
this.status = Rejected;
}
};
executor(resolve,reject);
},
}
三、初步实现 then 实例方法
按照上面对 then 实例方法的业务场景的简单分析,在 then 实例方法中调用回调函数时,还要把 executor 函数中业务代码的执行结果作为参数传递进去,那么要新增实例属性来存储业务代码的执行结果。另外执行成功的结果通过内置方法 resolve 的参数传入,其执行失败的原因通过内置方法 reject 的参数传入。
// 在这里用Symbol定义三种状态,防止外部改变状态
const Pending = Symbol('Pending'); // 进行中
const Fulfilled = Symbol('Fulfilled'); // 已成功
const Rejected = Symbol('Rejected'); // 已失败
class Promise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = Pending;//存储 Promise 的状态
this.value = undefined;//存储executor函数中业务代码执行成功的结果
this.reason = undefined;//存储executor函数中业务代码执行失败的原因
const resolve = value => {
// 只有当状态为 Pending 才会改变,来保证一旦状态改变就不会再变。
if (this.status === Pending) {
this.status = Fulfilled;
this.value = value;
}
};
const reject = value => {
// 只有当状态为 Pending 才会改变,来保证一旦状态改变就不会再变。
if (this.status === Pending) {
this.status = Rejected;
this.reason = value;
}
};
executor(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
if(this.status === Fulfilled){
if (onFulfilled && typeof onFulfilled === 'function') {
onFulfilled(this.value)
}
}
if(this.status === Rejected){
if (onRejected && typeof onRejected === 'function') {
onRejected(this.reason)
}
}
}
}
用个测试用例验证一下:
const test = new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{
resolve('"执行成功"')
})
test.then(res =>{
console.log(res)
})
在控制台上可以打印出 "执行成功",但是这里只处理了同步操作的 promise。如果在 executor 函数中传入一个异步操作的话呢?
const test = new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{
setTimeout(() =>{
resolve('"执行成功"')
},1000)
})
test.then(res =>{
console.log(res)
})
1 秒后,会发现控制台上并没有打印出 "执行成功",因为调用 then 实例方法时,Promise 的状态是 Pending ,虽然1秒后 Promise 的状态变为 Fulfilled ,但是 then 实例方法已经调用过了。
那么要怎么控制 then 实例方法中回调函数的执行时机。可以用发布者——订阅者的设计模式来实现。
当调用 then 实例方法时,如果 Promise 的状态是 Pending 时,先将成功回调函数和失败回调函数分别存放起来,在 executor 函数中异步任务执行结束,触发内置方法 resolve 或 reject,在其中去依次调用这些回调函数。
依据这个思路,再改一下代码。
// 在这里用Symbol定义三种状态,防止外部改变状态
const Pending = Symbol('Pending'); // 进行中
const Fulfilled = Symbol('Fulfilled'); // 已成功
const Rejected = Symbol('Rejected'); // 已失败
class Promise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = Pending;//存储 Promise 的状态
this.value = undefined;//存储executor函数中业务代码执行成功的结果
this.reason = undefined;//存储executor函数中业务代码执行失败的原因
this.onFulfilled = []; //executor函数中业务代码执行成功回调函数的集合
this.onRejected = []; //executor函数中业务代码执行失败回调函数的集合
const resolve = value => {
// 只有当状态为 Pending 才会改变,来保证一旦状态改变就不会再变。
if (this.status === Pending) {
this.status = Fulfilled;
this.value = value;
// 依次调用成功回调函数
this.onFulfilled.forEach(fn=>fn());
}
};
const reject = value => {
// 只有当状态为 Pending 才会改变,来保证一旦状态改变就不会再变。
if (this.status === Pending) {
this.status = Rejected;
this.reason = value;
// 依次调用失败回调函数
this.onRejected.forEach(fn=>fn());
}
};
executor(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
if(this.status === Fulfilled){
if (onFulfilled && typeof onFulfilled === 'function') {
onFulfilled(this.value)
}
}
if(this.status === Rejected){
if (onRejected && typeof onRejected === 'function') {
onRejected(this.reason)
}
}
if(this.status === Pending){
if (onFulfilled && typeof onFulfilled === 'function') {
this.onFulfilled.push(() =>{
onFulfilled(this.value)
})
}
if (onRejected && typeof onRejected === 'function') {
this.onRejected.push(() =>{
onRejected(this.reason)
})
}
}
}
}
在用上面的测试用例测试一下,1 秒之后控制台打印出 "执行成功"。代码逻辑正确。
四、实例方法 then 微任务的实现
由于原生的 Promise 是V8引擎提供的微任务,我们无法还原V8引擎的实现,所以这里使用 setTimeout 模拟异步,所以原生的是微任务,这里是宏任务。
另外 Promise A+ 规范3.1 中也提到了:
翻译一下
如果你想实现 promise 的微任务,可以 mutationObserver 替代 seiTimeout 来实现微任务。这里只是模拟异步而已。
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
if (this.status === Fulfilled) {
if (onFulfilled && typeof onFulfilled === 'function') {
setTimeout(() => {
onFulfilled(this.value)
}, 0)
}
}
if (this.status === Rejected) {
if (onRejected && typeof onRejected === 'function') {
setTimeout(() => {
onRejected(this.reason)
}, 0)
}
}
if (this.status === Pending) {
if (onFulfilled && typeof onFulfilled === 'function') {
this.onFulfilled.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
onFulfilled(this.value)
}, 0)
})
}
if (onRejected && typeof onRejected === 'function') {
this.onRejected.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
onRejected(this.reason)
}, 0)
})
}
}
}
五、实例方法 then 链式调用的实现
实例方法 then 链式调用有两个要求:
-
在实例方法
then后面可以直接使用实例方法then。 -
在前面一个实例方法
then返回一个值,不管是什么值,在后面一个实例方法then中都能获取到。
其实这种链式调用的实现很简单,在实例方法 then 返回一个新的 Promise 对象,把实例方法 then 返回的值 value,通过 resolve(value) 或 reject(value) 传递出去。
这个功能实现的难点是对实例方法 then 返回的值的类型的判断以及对应的处理。所以要写一个工具函数 handleValue 来专门处理实例方法 then 返回的值。
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
let promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === Fulfilled) {
if (onFulfilled && typeof onFulfilled === 'function') {
setTimeout(() => {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value);
handleValue(promise,x,resolve,reject);
}, 0)
}
}
if (this.status === Rejected) {
if (onRejected && typeof onRejected === 'function') {
setTimeout(() => {
let x = onRejected(this.reason);
handleValue(promise,x,resolve,reject);
}, 0)
}
}
if (this.status === Pending) {
if (onFulfilled && typeof onFulfilled === 'function') {
this.onFulfilled.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value);
handleValue(promise,x,resolve,reject);
}, 0)
})
}
if (onRejected && typeof onRejected === 'function') {
this.onRejected.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
let x = onRejected(this.reason);
handleValue(promise,x,resolve,reject);
}, 0)
})
}
}
})
return promise
}
如上,改造后实例方法 then 已经可以实现链式调用了。但是还没实现前一个实例方法 then 返回一个值,在后面一个实例方法 then 中能获取到。接下来在 handleValue 函数中实现。
按照 Promise/A+ 规范中对不同类型的返回值 X 的处理规则来实现 handleValue 函数,注意看代码注释。
const handleValue = (promise, x, resolve, reject) => {
// 循环引用,自己等待自己完成,会出错,用reject传递出错误原因
if (promise === x) {
return reject(new TypeError('检测到Promise的链式循环引用'))
}
// 确保只传递出去一次值
let once = false;
if ((x !== null && typeof x === 'object') || typeof x === 'function') {
// 防止重复去读取x.then
let then = x.then;
// 判断x是不是Promise
if (typeof then === 'function') {
//调用then实例方法处理Promise执行结果
then.call(x, y => {
if (once) return;
once = true;
// 防止Promise中Promise执行成功后又传递一个Promise过来,
// 要做递归解析。
handleValue(promise, y, resolve, reject);
}, r => {
if (once) return;
once = true;
reject(r);
})
} else {
// 如果x是个普通对象,直接调用resolve(x)
resolve(x);
}
} else {
// 如果x是个原始值,直接调用resolve(x)
resolve(x);
}
}
在上述代码中,判断typeof then === 'function'时其实是在判断返回的 x 是否为一个 Promise。如果没有 then 函数,x 即为普通值,直接返回 resolve(x)。如果有 then 函数,x 即为一个 Promise,就递归解析这个 Promise,直到 x 是一个普通值后作为最后的结果返回。
那么为什么用typeof then === 'function' 判断 x 是否为一个 Promise ,而不是用 x instanceof Promise 。 这是为了让 Promise 更具有通用性,所以一个 thenable 对象也可以看做是一个 Promise 。 thenable 对象就是一个拥有 then 方法的对象,如下代码所示例:
let thenable = {
then: function(resolve, reject){
resolve('执行成功')
}
}
在 thenable.then 方法中通过 resolve 传递执行成功的结果。但是 thenable 对象不是通过 Promise 类 new 出来的,故不能通过
x instanceof Promise 来判断是不是一个 Promise。
另外在Promise A+ 规范1.1 中也提到了:Promise 是一个具有 then 方法的对象或函数,其行为符合此规范。
六、实例方法 then 值穿透的实现
在上面的实现方法 then 链式调用的实现过程中,已经实现了值传递,当然是在 then 有传入参数的场景下。
那么在实例方法 then 中没传入参数,例:
const test = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('"执行成功"')
}, 3000)
})
test.then().then(res =>{
console.log(res)
})
此时后面的实例方法 then 依旧可以得到之前实例方法 then 返回的值,这就是所谓的值的穿透。正如上述例子中,控制台还是可以打印出 "执行成功"。
简单修改一下实例方法 then 就可以实现。
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === 'function' ? onFulfilled : v => v;
onRejected = typeof onRejected === 'function' ? onRejected : err => { throw err };;
let promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === Fulfilled) {
setTimeout(() => {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value);
handleValue(promise, x, resolve, reject);
}, 0)
}
if (this.status === Rejected) {
if (onRejected && typeof onRejected === 'function') {
setTimeout(() => {
let x = onRejected(this.reason);
handleValue(promise, x, resolve, reject);
}, 0)
}
}
if (this.status === Pending) {
this.onFulfilled.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value);
handleValue(promise, x, resolve, reject);
}, 0)
})
if (onRejected && typeof onRejected === 'function') {
this.onRejected.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
let x = onRejected(this.reason);
handleValue(promise, x, resolve, reject);
}, 0)
})
}
}
})
return promise
}
七、Promise 内部执行错误处理
上述代码都没对 Promise 内部执行错误进行捕获,可以用 try ... catch 语句来捕获错误,把错误用内置方法传递出去 reject,防止 Promise 内部执行错误无法追踪。
// 在这里用Symbol定义三种状态,防止外部改变状态
const Pending = Symbol('Pending'); // 进行中
const Fulfilled = Symbol('Fulfilled'); // 已成功
const Rejected = Symbol('Rejected'); // 已失败
const handleValue = (promise, x, resolve, reject) => {
// 循环引用,自己等待自己完成,会出错,用reject传递出错误原因
if (promise === x) {
return reject(new TypeError('检测到Promise的链式循环引用'))
}
// 确保只传递出去一次值
let once = false;
if ((x !== null && typeof x === 'object') || typeof x === 'function') {
try {
// 防止重复去读取x.then
let then = x.then;
// 判断x是不是Promise
if (typeof then === 'function') {
//调用then实例方法处理Promise执行结果
then.call(x, y => {
if (once) return;
once = true;
// 防止Promise中Promise执行成功后又传递一个Promise过来,
// 要做递归解析。
handleValue(promise, y, resolve, reject);
}, r => {
if (once) return;
once = true;
reject(r);
})
} else {
// 如果x是个普通对象,直接调用resolve(x)
resolve(x);
}
} catch (err) {
if (once) return;
once = true;
reject(err);
}
} else {
// 如果x是个原始值,直接调用resolve(x)
resolve(x);
}
}
class Promise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = Pending; //存储 Promise 的状态
this.value = undefined; //存储executor函数中业务代码执行成功的结果
this.reason = undefined; //存储executor函数中业务代码执行失败的原因
this.onFulfilled = []; //executor函数中业务代码执行成功回调函数的集合
this.onRejected = []; //executor函数中业务代码执行失败回调函数的集合
const resolve = value => {
// 只有当状态为 Pending 才会改变,来保证一旦状态改变就不会再变。
if (this.status === Pending) {
this.status = Fulfilled;
this.value = value;
// 依次调用成功回调函数
this.onFulfilled.forEach(fn => fn());
}
};
const reject = value => {
// 只有当状态为 Pending 才会改变,来保证一旦状态改变就不会再变。
if (this.status === Pending) {
this.status = Rejected;
this.reason = value;
// 依次调用失败回调函数
this.onRejected.forEach(fn => fn());
}
};
try {
executor(resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === 'function' ? onFulfilled : v => v;
onRejected = typeof onRejected === 'function' ? onRejected : err => {
throw err
};;
let promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === Fulfilled) {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value);
handleValue(promise, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}, 0)
}
if (this.status === Rejected) {
if (onRejected && typeof onRejected === 'function') {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = onRejected(this.reason);
handleValue(promise, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}, 0)
}
}
if (this.status === Pending) {
this.onFulfilled.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value);
handleValue(promise, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}, 0)
})
if (onRejected && typeof onRejected === 'function') {
this.onRejected.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = onRejected(this.reason);
handleValue(promise, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}, 0)
})
}
}
})
return promise
}
}
八、测试 Promise 是否符合规范
有专门的测试脚本可以测试所编写的代码是否符合 PromiseA+ 规范。
安装测试脚本:
npm install -g promises-aplus-tests
复制以下代码到 promise.js 文件中
// 在这里用Symbol定义三种状态,防止外部改变状态
const Pending = Symbol('Pending'); // 进行中
const Fulfilled = Symbol('Fulfilled'); // 已成功
const Rejected = Symbol('Rejected'); // 已失败
const handleValue = (promise, x, resolve, reject) => {
// 循环引用,自己等待自己完成,会出错,用reject传递出错误原因
if (promise === x) {
return reject(new TypeError('检测到Promise的链式循环引用'))
}
// 确保递归解析中只传递出去一次值
let once = false;
if ((x !== null && typeof x === 'object') || typeof x === 'function') {
try {
// 防止重复去读取x.then
let then = x.then;
// 判断x是不是Promise
if (typeof then === 'function') {
//调用then实例方法处理Promise执行结果
then.call(x, y => {
if (once) return;
once = true;
// 防止Promise中Promise执行成功后又传递一个Promise过来,
// 要做递归解析。
handleValue(promise, y, resolve, reject);
}, r => {
if (once) return;
once = true;
reject(r);
})
} else {
// 如果x是个普通对象,直接调用resolve(x)
resolve(x);
}
} catch (err) {
if (once) return;
once = true;
reject(err);
}
} else {
// 如果x是个原始值,直接调用resolve(x)
resolve(x);
}
}
class Promise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = Pending; //存储 Promise 的状态
this.value = undefined; //存储executor函数中业务代码执行成功的结果
this.reason = undefined; //存储executor函数中业务代码执行失败的原因
this.onFulfilled = []; //executor函数中业务代码执行成功回调函数的集合
this.onRejected = []; //executor函数中业务代码执行失败回调函数的集合
const resolve = value => {
// 只有当状态为 Pending 才会改变,来保证一旦状态改变就不会再变。
if (this.status === Pending) {
this.status = Fulfilled;
this.value = value;
// 依次调用成功回调函数
this.onFulfilled.forEach(fn => fn());
}
};
const reject = value => {
// 只有当状态为 Pending 才会改变,来保证一旦状态改变就不会再变。
if (this.status === Pending) {
this.status = Rejected;
this.reason = value;
// 依次调用失败回调函数
this.onRejected.forEach(fn => fn());
}
};
try {
executor(resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === 'function' ? onFulfilled : v => v;
onRejected = typeof onRejected === 'function' ? onRejected : err => {
throw err
};;
let promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === Fulfilled) {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value);
handleValue(promise, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}, 0)
}
if (this.status === Rejected) {
if (onRejected && typeof onRejected === 'function') {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = onRejected(this.reason);
handleValue(promise, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}, 0)
}
}
if (this.status === Pending) {
this.onFulfilled.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value);
handleValue(promise, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}, 0)
})
if (onRejected && typeof onRejected === 'function') {
this.onRejected.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = onRejected(this.reason);
handleValue(promise, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}, 0)
})
}
}
})
return promise
}
static defer(){
let dfd = {};
dfd.promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
dfd.resolve = resolve;
dfd.reject = reject;
});
return dfd;
}
static deferred(){
let dfd = {};
dfd.promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
dfd.resolve = resolve;
dfd.reject = reject;
});
return dfd;
}
}
module.exports = Promise;
那么在对应的目录执行以下命令:
promises-aplus-tests promise.js
执行结果如下所示
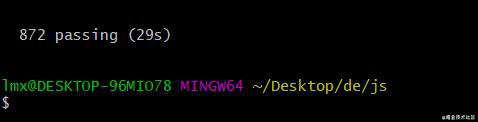
872 个测试用例全部通过。
九、实例方法 catch 的实现
this.catch就是 this.then(null, onRejected)的别名。
catch(onRejected){
this.then(null, onRejected)
}
十、静态方法 Promise.resolve() 的实现
先回顾一下 Promise.resolve() 的用法。
Promise.resolve() 的作用是把传入的参数转成一个 Promise 对象。
-
如果参数是一个 Promise 实例,直接返回这个 Promise 实例。
-
如果参数是一个 thenable 对象,
thenable 对象指的是具有
then方法的对象,例如let thenable = { then(resolve,reject){ resolve (42); } }Promise.resolve()方法会将这个对象转为 Promise 对象,然后立即执行 thenable 对象then方法。 -
参数不是具有
then方法的对象或根本不是对象,那么Promise.resolve()方法返回个新的 Promise 实例,状态为已成功,并把参数传递出去。 -
不带有任何参数,
Promise.resolve()方法允许在调用时不带有参数而直接返回个新的 Promise 实例,状态为已成功。
根据其的用法很容易实现 Promise.resolve()
class Promise{
//...
static resolve(param) {
if (param instanceof Promise){
return param;
}
return new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{
if(
param &&
Object.prototype.toString.call(param) === '[object Object]' &&
typeof param.then === 'function'
){
setTimeout(() =>{
param.then(resolve,reject)
},0)
}else{
resolve(param)
}
})
}
}
十一、静态方法 Promise.reject() 的实现
先回顾一下 Promise.reject() 的用法:返回一个新的 Promise 实例,状态为已失败,并把参数作为失败的原因传递出去。
根据其的用法很容易实现 Promise.reject()
class Promise{
//...
static reject(param){
return new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{
reject(param)
})
}
}
十二、静态方法 Promise.all() 的实现
先回顾一下 Promise.all() 的用法。
Promise.all() 的作用是把多个 Promise 实例包装成一个新的 Promise 实例。
例如:p = Promise.all(p1,p2,p3),其中 p1、p2、p3 不是 Promise 实例的,内部会通过 Promise.resolve() 将其转成 Promise 实例。p 的状态由 p1、p2、p3 决定, 分成两种情况。
-
只有 p1、p2、p3 的状态都变为已成功, p 的状态才会变为已成功 ,此 pl p2 p3 的返回值组成一个数组,传递给 p 的回调函数。
-
只要 pl p2 p3 中有一个的状态变为已失败,p 的状态就会变为已失败,此时 pl p2 p3 中第一个状态变为已失败的返回值会
传递给 p 的回调函数。
class Promise {
//...
static all(promises) {
//将参数promises转为一个真正的数组
promises = Array.from(promises);
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
let value = [];
const length = promises.length;
if (length) {
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Promise.resolve(promises[i]).then(
res => {
value.push(res);
if (value.length == length) {
resolve(value);
}
},
err => {
reject(err)
return;
}
)
}
} else {
resolve(value)
}
})
}
}
十三、静态方法 Promise.race() 的实现
先回顾一下 Promise.race() 的用法。
Promise.race() 的作用是把多个 Promise 实例包装成一个新的 Promise 实例。
例如:p = Promise.all(p1,p2,p3),其中 p1、p2、p3 不是 Promise 实例的,内部会通过 Promise.resolve() 将其转成 Promise 实例。p 的状态由 p1、p2、p3 决定, 只要 pl p2 p3 中有一个的状态改变,p 的状态马上就会对应改变,此时 pl p2 p3 中第一个状态改变的返回值会传递给 p 的回调函数。
class Promise {
//...
static race(promises) {
//将参数promises转为一个真正的数组
promises = Array.from(promises);
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const length = promises.length;
if (length) {
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Promise.resolve(promises[i]).then(
res => {
resolve(res);
return;
},
err => {
reject(err)
return;
}
)
}
} else {
resolve(value)
}
})
}
}
十四、完整代码
// 在这里用Symbol定义三种状态,防止外部改变状态
const Pending = Symbol('Pending'); // 进行中
const Fulfilled = Symbol('Fulfilled'); // 已成功
const Rejected = Symbol('Rejected'); // 已失败
const handleValue = (promise, x, resolve, reject) => {
// 循环引用,自己等待自己完成,会出错,用reject传递出错误原因
if (promise === x) {
return reject(new TypeError('检测到Promise的链式循环引用'))
}
// 确保递归解析中只传递出去一次值
let once = false;
if ((x !== null && typeof x === 'object') || typeof x === 'function') {
try {
// 防止重复去读取x.then
let then = x.then;
// 判断x是不是Promise
if (typeof then === 'function') {
//调用then实例方法处理Promise执行结果
then.call(x, y => {
if (once) return;
once = true;
// 防止Promise中Promise执行成功后又传递一个Promise过来,
// 要做递归解析。
handleValue(promise, y, resolve, reject);
}, r => {
if (once) return;
once = true;
reject(r);
})
} else {
// 如果x是个普通对象,直接调用resolve(x)
resolve(x);
}
} catch (err) {
if (once) return;
once = true;
reject(err);
}
} else {
// 如果x是个原始值,直接调用resolve(x)
resolve(x);
}
}
class Promise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = Pending; //存储 Promise 的状态
this.value = undefined; //存储executor函数中业务代码执行成功的结果
this.reason = undefined; //存储executor函数中业务代码执行失败的原因
this.onFulfilled = []; //executor函数中业务代码执行成功回调函数的集合
this.onRejected = []; //executor函数中业务代码执行失败回调函数的集合
const resolve = value => {
// 只有当状态为 Pending 才会改变,来保证一旦状态改变就不会再变。
if (this.status === Pending) {
this.status = Fulfilled;
this.value = value;
// 依次调用成功回调函数
this.onFulfilled.forEach(fn => fn());
}
};
const reject = value => {
// 只有当状态为 Pending 才会改变,来保证一旦状态改变就不会再变。
if (this.status === Pending) {
this.status = Rejected;
this.reason = value;
// 依次调用失败回调函数
this.onRejected.forEach(fn => fn());
}
};
try {
executor(resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === 'function' ? onFulfilled : v => v;
onRejected = typeof onRejected === 'function' ? onRejected : err => {
throw err
};;
let promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === Fulfilled) {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value);
handleValue(promise, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}, 0)
}
if (this.status === Rejected) {
if (onRejected && typeof onRejected === 'function') {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = onRejected(this.reason);
handleValue(promise, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}, 0)
}
}
if (this.status === Pending) {
this.onFulfilled.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value);
handleValue(promise, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}, 0)
})
if (onRejected && typeof onRejected === 'function') {
this.onRejected.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = onRejected(this.reason);
handleValue(promise, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}, 0)
})
}
}
})
return promise
}
static resolve(param) {
if (param instanceof Promise){
return param;
}
return new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{
if(
param &&
Object.prototype.toString.call(param) === '[object Object]' &&
typeof param.then === 'function'
){
setTimeout(() =>{
param.then(resolve,reject)
},0)
}else{
resolve(param)
}
})
}
static reject(param){
return new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{
reject(param)
})
}
static all(promises) {
//将参数promises转为一个真正的数组
promises = Array.from(promises);
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
let value = [];
const length = promises.length;
if (length) {
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Promise.resolve(promises[i]).then(
res => {
value.push(res);
if (value.length == length) {
resolve(value);
}
},
err => {
reject(err)
return;
}
)
}
} else {
resolve(value)
}
})
}
static race(promises) {
//将参数promises转为一个真正的数组
promises = Array.from(promises);
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const length = promises.length;
if (length) {
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Promise.resolve(promises[i]).then(
res => {
resolve(res);
return;
},
err => {
reject(err)
return;
}
)
}
} else {
resolve(value)
}
})
}
}
常见问题FAQ
- 免费下载或者VIP会员专享资源能否直接商用?
- 本站所有资源版权均属于原作者所有,这里所提供资源均只能用于参考学习用,请勿直接商用。若由于商用引起版权纠纷,一切责任均由使用者承担。更多说明请参考 VIP介绍。
- 提示下载完但解压或打开不了?
- 找不到素材资源介绍文章里的示例图片?
- 模板不会安装或需要功能定制以及二次开发?






发表评论
还没有评论,快来抢沙发吧!