最近恰好在写 Kraken 事件相关的功能,把 Flutter 的事件机制整理一下做一个总结。
之前在上一篇《Flutter 事件机制以及 Kraken 如何实现基于 web 标准的点击事件》 里面已经把 Flutter 如何从硬件层面把一个事件传递下发到 dart 以及如何通过 hittest 确定这次事件对应的所有元素。总的来说,Flutter 会把事件塞入一个 Pipe 中,然后取出里面的事件,对整棵树遍历进行 hittest 得到结果。最后对得到的结果进行 dispatch。
那么具体的手势如何触发呢?
GestureDetector
Flutter 本身为 Widget 做了一套手势处理器 GestureDetector,在原始指针之上为单击、双击、滑动、长按等手势做了一套统一的封装,方便开发者可以直接调用。
而且每一种手势都做了细粒度的拆解,比如点击事件会通过 onTapDown 、onTapUp、 onTap、onTapCancel等方法分别拆解成点击的 down 事件,点击 up 事件、点击事件以及点击取消事件,对应到 Web 就是 touchstart、touchend 、click等事件,但是不同的是在 Flutter 中会通过竞技场得到一个获胜的元素,而其他元素在 GestureDetector 的方法中是不会像 Web 一样进行捕获冒泡的事件传递的。
接下来我们来看一下 GestureDetector 这个类。
class GestureDetector extends StatelessWidget {
GestureDetector({
Key key,
this.child,
this.onTapDown,
this.onTapUp,
this.onTap,
this.onTapCancel,
this.onSecondaryTapDown,
this.onSecondaryTapUp,
this.onSecondaryTapCancel,
this.onDoubleTap,
this.onLongPress,
this.onLongPressStart,
this.onLongPressMoveUpdate,
this.onLongPressUp,
this.onLongPressEnd,
this.onVerticalDragDown,
this.onVerticalDragStart,
this.onVerticalDragUpdate,
this.onVerticalDragEnd,
this.onVerticalDragCancel,
this.onHorizontalDragDown,
this.onHorizontalDragStart,
this.onHorizontalDragUpdate,
this.onHorizontalDragEnd,
this.onHorizontalDragCancel,
this.onForcePressStart,
this.onForcePressPeak,
this.onForcePressUpdate,
this.onForcePressEnd,
this.onPanDown,
this.onPanStart,
this.onPanUpdate,
this.onPanEnd,
this.onPanCancel,
this.onScaleStart,
this.onScaleUpdate,
this.onScaleEnd,
this.behavior,
this.excludeFromSemantics = false,
this.dragStartBehavior = DragStartBehavior.start,
})
/// ...
}
那么,GestureDetector 怎么用?
譬如说我们需要调用一个点击事件,在 widget 中我们可以这样写:
GestureDetector(
//监听点击事件
onTap: () => {
print("点击事件")
},
child: Center(
child: Container(
color: Colors.blue,
width: 100.0,
height: 50.0,
),
),
),
纵向滑动监听时间,在 widget 中可以这样写:
GestureDetector(
//监听点击事件
onVerticalDragUpdate: (DragUpdateDetails details) => {
print("纵滑")
},
child: Center(
child: Container(
color: Colors.blue,
width: 100.0,
height: 50.0,
),
),
),
GestureDetector 本身已经做了大量封装,在 widget 体系下使用十分方便,可以覆盖大量的业务所需的手势场景。
下面我们来看一下 GestureDetector 的具体实现。
GestureDetector 实现原理
首先来看一下 GestureDetector 的实现
class GestureDetector {
/// ...
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final Map<Type, GestureRecognizerFactory> gestures = <Type, GestureRecognizerFactory>{};
/// 点击事件
if (
onTapDown != null ||
onTapUp != null ||
onTap != null ||
onTapCancel != null ||
onSecondaryTapDown != null ||
onSecondaryTapUp != null ||
onSecondaryTapCancel != null
) {
gestures[TapGestureRecognizer] = GestureRecognizerFactoryWithHandlers<TapGestureRecognizer>(
() => TapGestureRecognizer(debugOwner: this),
(TapGestureRecognizer instance) {
instance
..onTapDown = onTapDown
..onTapUp = onTapUp
..onTap = onTap
..onTapCancel = onTapCancel
..onSecondaryTapDown = onSecondaryTapDown
..onSecondaryTapUp = onSecondaryTapUp
..onSecondaryTapCancel = onSecondaryTapCancel;
},
);
}
/// 双击事件
if (onDoubleTap != null) {
gestures[DoubleTapGestureRecognizer] = GestureRecognizerFactoryWithHandlers<DoubleTapGestureRecognizer>(
() => DoubleTapGestureRecognizer(debugOwner: this),
(DoubleTapGestureRecognizer instance) {
instance.onDoubleTap = onDoubleTap;
},
);
}
/// 长按事件
if (onLongPress != null ||
onLongPressUp != null ||
onLongPressStart != null ||
onLongPressMoveUpdate != null ||
onLongPressEnd != null) {
gestures[LongPressGestureRecognizer] = GestureRecognizerFactoryWithHandlers<LongPressGestureRecognizer>(
() => LongPressGestureRecognizer(debugOwner: this),
(LongPressGestureRecognizer instance) {
instance
..onLongPress = onLongPress
..onLongPressStart = onLongPressStart
..onLongPressMoveUpdate = onLongPressMoveUpdate
..onLongPressEnd =onLongPressEnd
..onLongPressUp = onLongPressUp;
},
);
}
/// 垂直方向的滑动事件
if (onVerticalDragDown != null ||
onVerticalDragStart != null ||
onVerticalDragUpdate != null ||
onVerticalDragEnd != null ||
onVerticalDragCancel != null) {
gestures[VerticalDragGestureRecognizer] = GestureRecognizerFactoryWithHandlers<VerticalDragGestureRecognizer>(
() => VerticalDragGestureRecognizer(debugOwner: this),
(VerticalDragGestureRecognizer instance) {
instance
..onDown = onVerticalDragDown
..onStart = onVerticalDragStart
..onUpdate = onVerticalDragUpdate
..onEnd = onVerticalDragEnd
..onCancel = onVerticalDragCancel
..dragStartBehavior = dragStartBehavior;
},
);
}
/// 水平方向的滑动事件
if (onHorizontalDragDown != null ||
onHorizontalDragStart != null ||
onHorizontalDragUpdate != null ||
onHorizontalDragEnd != null ||
onHorizontalDragCancel != null) {
gestures[HorizontalDragGestureRecognizer] = GestureRecognizerFactoryWithHandlers<HorizontalDragGestureRecognizer>(
() => HorizontalDragGestureRecognizer(debugOwner: this),
(HorizontalDragGestureRecognizer instance) {
instance
..onDown = onHorizontalDragDown
..onStart = onHorizontalDragStart
..onUpdate = onHorizontalDragUpdate
..onEnd = onHorizontalDragEnd
..onCancel = onHorizontalDragCancel
..dragStartBehavior = dragStartBehavior;
},
);
}
/// 水平以及垂直方向的滑动事件
if (onPanDown != null ||
onPanStart != null ||
onPanUpdate != null ||
onPanEnd != null ||
onPanCancel != null) {
gestures[PanGestureRecognizer] = GestureRecognizerFactoryWithHandlers<PanGestureRecognizer>(
() => PanGestureRecognizer(debugOwner: this),
(PanGestureRecognizer instance) {
instance
..onDown = onPanDown
..onStart = onPanStart
..onUpdate = onPanUpdate
..onEnd = onPanEnd
..onCancel = onPanCancel
..dragStartBehavior = dragStartBehavior;
},
);
}
/// 缩放事件
if (onScaleStart != null || onScaleUpdate != null || onScaleEnd != null) {
gestures[ScaleGestureRecognizer] = GestureRecognizerFactoryWithHandlers<ScaleGestureRecognizer>(
() => ScaleGestureRecognizer(debugOwner: this),
(ScaleGestureRecognizer instance) {
instance
..onStart = onScaleStart
..onUpdate = onScaleUpdate
..onEnd = onScaleEnd;
},
);
}
/// 用力按压事件(需要硬件支持)
if (onForcePressStart != null ||
onForcePressPeak != null ||
onForcePressUpdate != null ||
onForcePressEnd != null) {
gestures[ForcePressGestureRecognizer] = GestureRecognizerFactoryWithHandlers<ForcePressGestureRecognizer>(
() => ForcePressGestureRecognizer(debugOwner: this),
(ForcePressGestureRecognizer instance) {
instance
..onStart = onForcePressStart
..onPeak = onForcePressPeak
..onUpdate = onForcePressUpdate
..onEnd = onForcePressEnd;
},
);
}
return RawGestureDetector(
gestures: gestures,
behavior: behavior,
excludeFromSemantics: excludeFromSemantics,
child: child,
);
}
}
在 build 方法中,GestureDetector 会通过工厂类生成一堆 gestures,每个 gesture 会分别处理不同的手势,譬如说点击(包含点击的 down、up、tap 等等)、双击、长按等等,最终会把这些 gestures 传入到 RawGestureDetector 这个类中。
class RawGestureDetector extends StatefulWidget {
/// ...
@override
RawGestureDetectorState createState() => RawGestureDetectorState();
}
class RawGestureDetectorState extends State<RawGestureDetector> {
/// ...
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
Widget result = Listener(
onPointerDown: _handlePointerDown,
behavior: widget.behavior ?? _defaultBehavior,
child: widget.child,
);
if (!widget.excludeFromSemantics)
result = _GestureSemantics(
child: result,
assignSemantics: _updateSemanticsForRenderObject,
);
return result;
}
void _handlePointerDown(PointerDownEvent event) {
assert(_recognizers != null);
for (final GestureRecognizer recognizer in _recognizers.values)
recognizer.addPointer(event);
}
}
不难发现,最终会通过 Listener 这个类去监听手势的 down 事件,放在触摸屏的场景,也就是当手接触到屏幕的一刹那会触发这个 down 事件,在 down 事件中做了一件事情,遍历之前生成的所有 gestures,然后执行每个 gesture 的 addPointer 方法。
那么有的小伙伴就会好奇了,为什么我们只需要对 down 这个事件做处理而不需要对 up、move 等等事件处理,不处理那些事件我们怎么判断用户到底做了什么手势呢?
其实不然,startTrackingPointer 方法中会将 handleEvent 事件加入到路由表中,而路由表最终会调用到 handleEvent 函数,move、up 以及 cancel 等事件都会最终通过路由表分发到 handleEvent 函数中,由这个函数做处理。
startTrackingPointer 在 OneSequenceGestureRecognizer 类中实现。
void startTrackingPointer(int pointer, [Matrix4 transform]) {
GestureBinding.instance.pointerRouter.addRoute(pointer, handleEvent, transform);
_trackedPointers.add(pointer);
assert(!_entries.containsValue(pointer));
_entries[pointer] = _addPointerToArena(pointer);
}
除了把事件放入路由表以外,startTrackingPointer 方法还会将当前的 pointer 存入到竞技场中,解决手势竞争的问题,这个竞技场的作用以及原理笔者后面单独分析。
当手势点击触发 down 以后会发生什么事情呢?
for (final GestureRecognizer recognizer in _recognizers.values)
recognizer.addPointer(event);
这里的 _recognizers 是一个 map,里面存放了上了我们提到的一些列的 GestureRecognizer。GestureRecognizer 是上述的所有的手势识别器的基类。手势触发 down 操作后会便利目前节点所有的手势识别器(工厂类注册的地方已经做了优化,没有注册事件是不会生成识别器的),并调用每个手势识别器的 addPointer 方法。
abstract class GestureRecognizer extends GestureArenaMember with DiagnosticableTreeMixin {
/// ...
void addPointer(PointerDownEvent event) {
_pointerToKind[event.pointer] = event.kind;
if (isPointerAllowed(event)) {
addAllowedPointer(event);
} else {
handleNonAllowedPointer(event);
}
}
}
addPointer 会调用手势识别器的 isPointerAllowed 方法,这个依赖继承类的实现,用以判断当前 pointer 是否被允许,允许则走 addAllowedPointer 流程,否者直接 handleNonAllowedPointer。GestureRecognizer 是一个抽象类,这两个方法完全依赖上层的继承去实现。
每个手势识别器在 GestureRecognizer 之上实现了一套自己的手势识别规则,他们大致的继承关系如下。
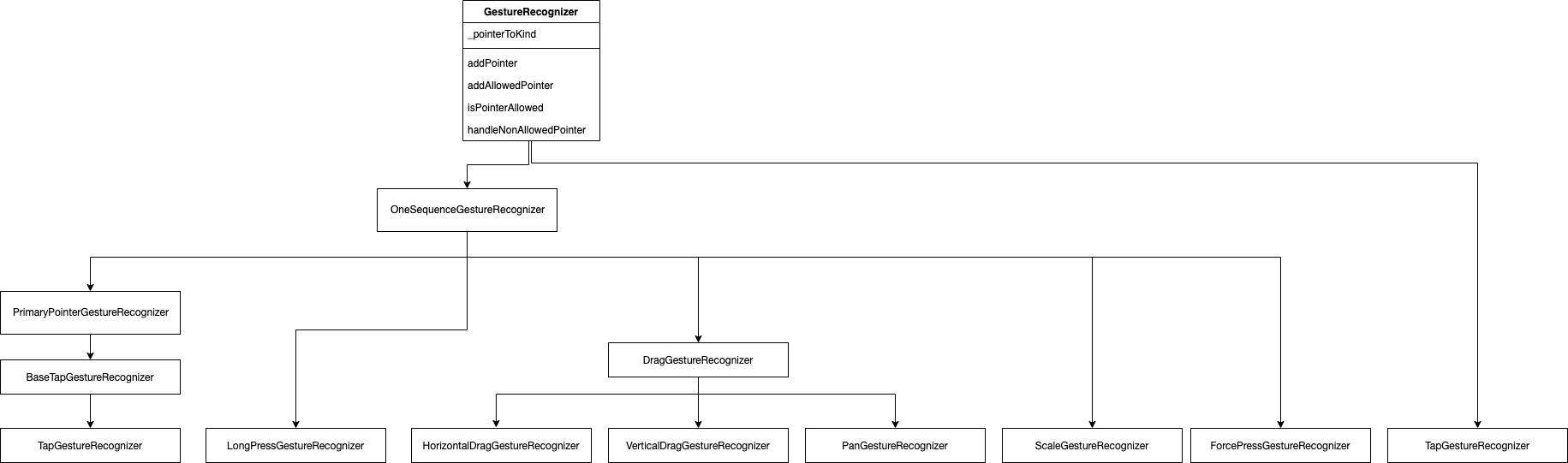
我们以点击事件 TapGestureRecognizer 为例来说一下具体手势识别器如何在 GestureRecognizer 扩展以及如何新增手势识别器。
来看一下 TapGestureRecognizer 实现的 isPointerAllowed,判断当前节点是否有注册相关事件,没有事件就不需要走其余流程了。
@override
bool isPointerAllowed(PointerDownEvent event) {
switch (event.buttons) {
case kPrimaryButton:
if (onTapDown == null &&
onTap == null &&
onTapUp == null &&
onTapCancel == null)
return false;
break;
case kSecondaryButton:
if (onSecondaryTap == null &&
onSecondaryTapDown == null &&
onSecondaryTapUp == null &&
onSecondaryTapCancel == null)
return false;
break;
case kTertiaryButton:
if (onTertiaryTapDown == null &&
onTertiaryTapUp == null &&
onTertiaryTapCancel == null)
return false;
break;
default:
return false;
}
return super.isPointerAllowed(event);
}
然后是它的 addAllowedPointer ,startTrackingPointer 前面已经介绍了,主要是往路由中注册事件。接下来会将标识位判断以及赋值,保证不会多个 pointer 操作(物理表现就是比如多只手做不同手势操作当前节点)。接下来会保存初始状态(用以判断手势)并且有一个定时器来处理超时的异常情况。
@override
void addAllowedPointer(PointerDownEvent event) {
startTrackingPointer(event.pointer, event.transform);
if (state == GestureRecognizerState.ready) {
state = GestureRecognizerState.possible;
primaryPointer = event.pointer;
initialPosition = OffsetPair(local: event.localPosition, global: event.position);
if (deadline != null)
_timer = Timer(deadline!, () => didExceedDeadlineWithEvent(event));
}
}
handleNonAllowedPointer 就不用多说了,不允许当前 pointer 操作的话,直接拒绝。当然,如果自定义去扩展手势,这里可以做别的各种想在 pointer 被拒绝时处理的操作。
@override
void handleNonAllowedPointer(PointerDownEvent event) {
resolve(GestureDisposition.rejected);
}
上面几个方法主要是处理当前 pointer 是否能接受,以及接受或者不接受的处理流程,不接受一般直接 reject 即可,接受的流程在前面讲过,会将当前 pointer 注册到路由中,同时也会加入到【竞技场】中,接下来一系列 pointer 就会触发 handleEvent 事件了。
@override
void handleEvent(PointerEvent event) {
assert(state != GestureRecognizerState.ready);
if (state == GestureRecognizerState.possible && event.pointer == primaryPointer) {
final bool isPreAcceptSlopPastTolerance =
!_gestureAccepted &&
preAcceptSlopTolerance != null &&
_getGlobalDistance(event) > preAcceptSlopTolerance!;
final bool isPostAcceptSlopPastTolerance =
_gestureAccepted &&
postAcceptSlopTolerance != null &&
_getGlobalDistance(event) > postAcceptSlopTolerance!;
if (event is PointerMoveEvent && (isPreAcceptSlopPastTolerance || isPostAcceptSlopPastTolerance)) {
resolve(GestureDisposition.rejected);
stopTrackingPointer(primaryPointer!);
} else {
handlePrimaryPointer(event);
}
}
stopTrackingIfPointerNoLongerDown(event);
}
这里以 TapGestureRecognizer 为例,这里会判断是否 move 并超过默认的 18 个物理像素,因为触摸屏手指触碰时会存在飘的情况,实际上肯定会触发 move 的,不能简单地以 down 跟 up 来判断是否是点击事件。至于为什么是 18 个物理像素,经验所得(逃
确认是点击手势,然后就是 handlePrimaryPointer 了,会调用 stopTrackingPointer 移除路由信息等操作,并把整个手势的 pointer 集合清空,最后就是触发最早注册的回调函数了。
其余的手势识别器原理上都类似,都是在 pointer 之上做一系列的封装,通过一系列点来做具体的手势的判断。
常见问题FAQ
- 免费下载或者VIP会员专享资源能否直接商用?
- 本站所有资源版权均属于原作者所有,这里所提供资源均只能用于参考学习用,请勿直接商用。若由于商用引起版权纠纷,一切责任均由使用者承担。更多说明请参考 VIP介绍。
- 提示下载完但解压或打开不了?
- 找不到素材资源介绍文章里的示例图片?
- 模板不会安装或需要功能定制以及二次开发?






发表评论
还没有评论,快来抢沙发吧!