前言
在Flutter开发中,Container作为一个容器类的Widget,有点类似HTML的div,在项目中也是高频使用;那在使用过程中,你是否有过下面的这些疑问:
- Container是什么,它如何实现的?
- Container的大小约束规则是什么?下面几种情况你知道为什么吗?
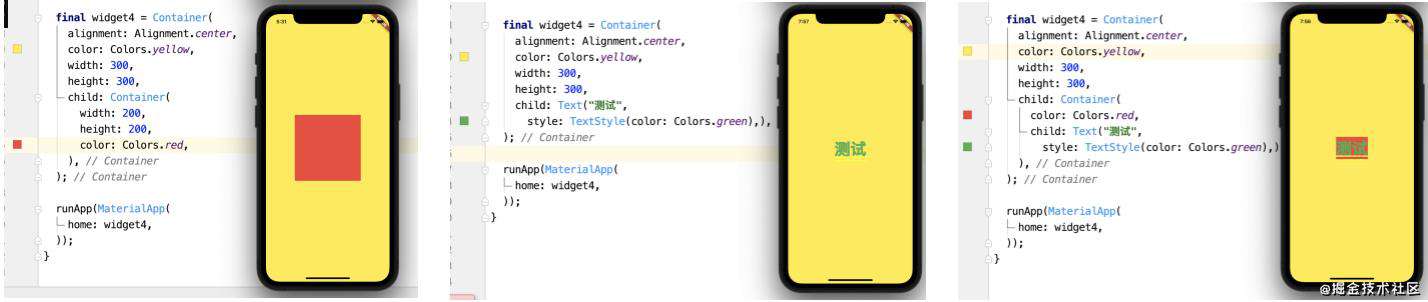
Container介绍
首先我们来看一下Contaienr是什么:
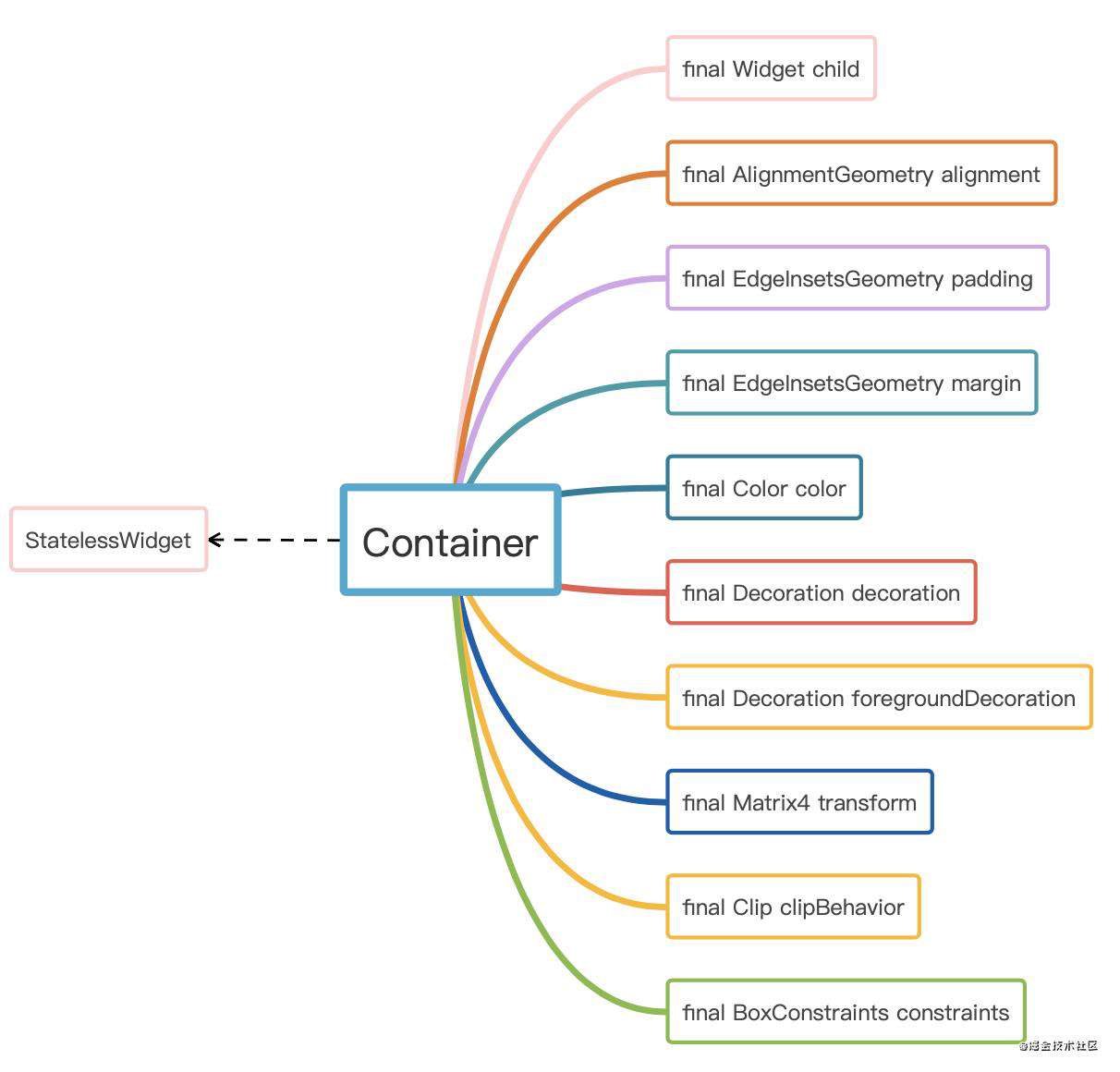 可以看到,通过上面可以知道,Container是继承自StatelessWidget的widget,有丰富的属性配置,通过这些属性,我们可以设置前景,背景,颜色,内外边距,裁剪方式,对齐方式等。而且由于Container是继承自StatelessWidget,所以它并不能构建renderObject,不能直接参与绘制,所以看一下它的
可以看到,通过上面可以知道,Container是继承自StatelessWidget的widget,有丰富的属性配置,通过这些属性,我们可以设置前景,背景,颜色,内外边距,裁剪方式,对齐方式等。而且由于Container是继承自StatelessWidget,所以它并不能构建renderObject,不能直接参与绘制,所以看一下它的build()函数的实现:
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
Widget current = child;
if (child == null && (constraints == null || !constraints.isTight)) {
current = LimitedBox(
maxWidth: 0.0,
maxHeight: 0.0,
child: ConstrainedBox(constraints: const BoxConstraints.expand()),
);
}
if (alignment != null)
current = Align(alignment: alignment, child: current);
final EdgeInsetsGeometry effectivePadding = _paddingIncludingDecoration;
if (effectivePadding != null)
current = Padding(padding: effectivePadding, child: current);
if (color != null)
current = ColoredBox(color: color, child: current);
if (clipBehavior != Clip.none) {
assert(decoration != null);
current = ClipPath(
clipper: _DecorationClipper(
textDirection: Directionality.of(context),
decoration: decoration
),
clipBehavior: clipBehavior,
child: current,
);
}
if (decoration != null)
current = DecoratedBox(decoration: decoration, child: current);
if (foregroundDecoration != null) {
current = DecoratedBox(
decoration: foregroundDecoration,
position: DecorationPosition.foreground,
child: current,
);
}
if (constraints != null)
current = ConstrainedBox(constraints: constraints, child: current);
if (margin != null)
current = Padding(padding: margin, child: current);
if (transform != null)
current = Transform(transform: transform, child: current);
return current;
}
通过build()函数可以知道,Container只是对不同的renderObjectWidget的组合封装。这简化了我们布局时的widget嵌套层数;其次,注意这里各种widgets的组合的先后顺序,flutter的“盒模型”没有内外边距的概念,边距的实现是通过嵌套一个“盒子”实现的,我们能看到边距的效果,就是因为这里的顺序,是先嵌套了边距widget,这个widget的大小是child的大小加上我们设置的"padding"。关于大小约束在后面再具体聊。
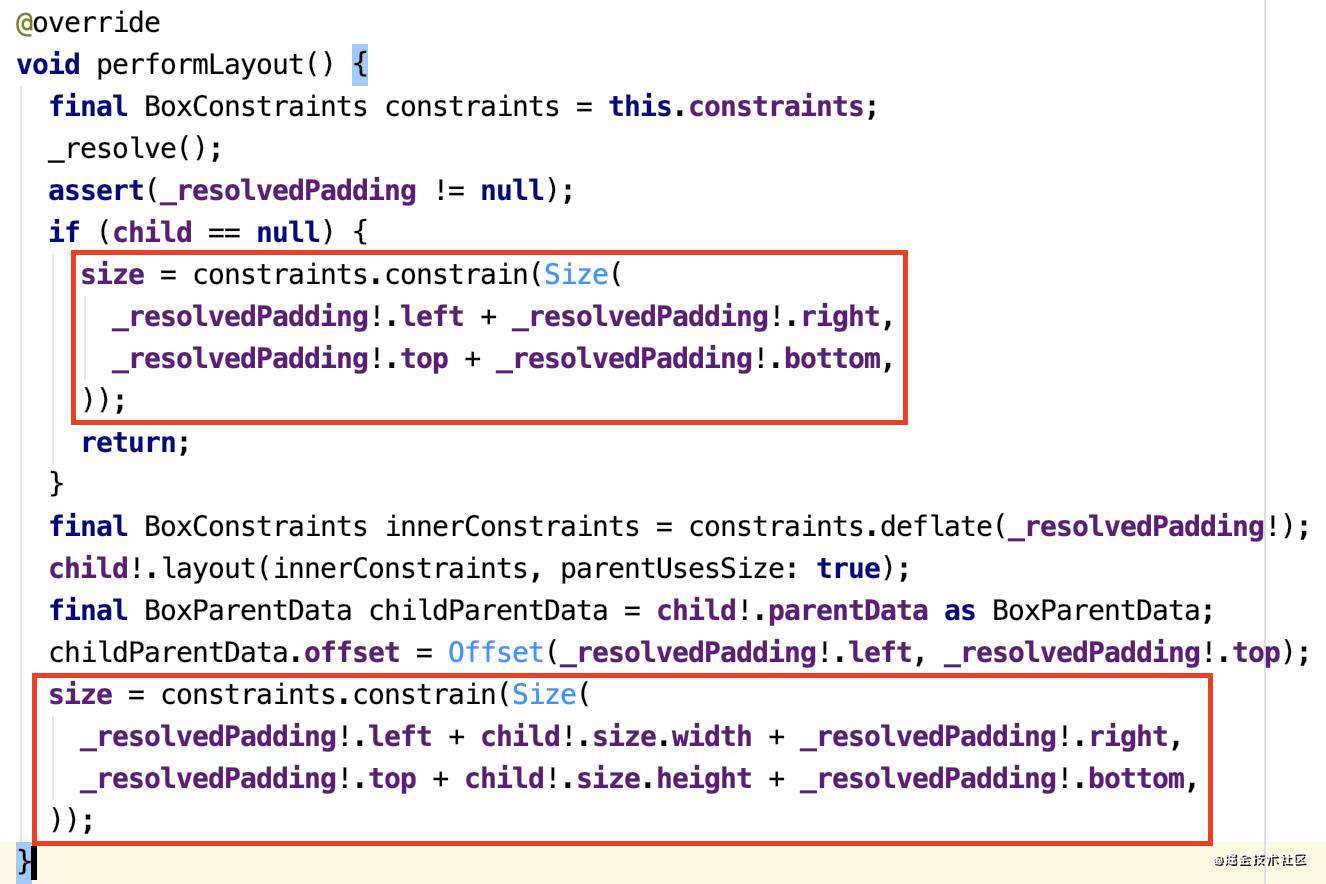
大小和约束的流程
在学习大小约束之前,我们需要知道renderObject的布局计算流程。我们定位到RenderObject类中,定位到函数:
abstract class RenderObject extends AbstractNode with DiagnosticableTreeMixin implements HitTestTarget {
void layout(Constraints constraints, { bool parentUsesSize = false }) {
if (!kReleaseMode && debugProfileLayoutsEnabled)
Timeline.startSync('$runtimeType', arguments: timelineArgumentsIndicatingLandmarkEvent);
...
RenderObject? relayoutBoundary;
if (!parentUsesSize || sizedByParent || constraints.isTight || parent is! RenderObject) {
relayoutBoundary = this;
} else {
relayoutBoundary = (parent as RenderObject)._relayoutBoundary;
}
...
if (!_needsLayout && constraints == _constraints && relayoutBoundary == _relayoutBoundary) {
...
if (!kReleaseMode && debugProfileLayoutsEnabled)
Timeline.finishSync();
return;
}
_constraints = constraints;
...
if (sizedByParent) {
...
try {
performResize();
...
} catch (e, stack) {
...
}
...
}
...
try {
performLayout();
...
} catch (e, stack) {
...
}
...
_needsLayout = false;
markNeedsPaint();
if (!kReleaseMode && debugProfileLayoutsEnabled)
Timeline.finishSync();
}
@protected
void performResize();
@protected
void performLayout();
void paint(PaintingContext context, Offset offset) { }
}
找一个layout的调用:

 好了,我们来分析一下:
好了,我们来分析一下:layout函数的入参是一个约束,可以从外部获取约束,然后再调用performResize和performLayout,这里官方要求子类不能重写layout,而是直接重写performResize或performLayout;主要的作用是:把自己的约束传给子类;从子类获取大小;继续绘制子类,最后通过类的paint函数进行绘制。整个过程递归,就完成了各个renderObject的大小和约束的计算并绘制。
约束规则
偷个懒直接看Flutter官网的介绍:

常见问题FAQ
- 免费下载或者VIP会员专享资源能否直接商用?
- 本站所有资源版权均属于原作者所有,这里所提供资源均只能用于参考学习用,请勿直接商用。若由于商用引起版权纠纷,一切责任均由使用者承担。更多说明请参考 VIP介绍。
- 提示下载完但解压或打开不了?
- 找不到素材资源介绍文章里的示例图片?
- 模板不会安装或需要功能定制以及二次开发?






发表评论
还没有评论,快来抢沙发吧!