接上篇 —— dayjs 源码解析(三):插件(上) —— 继续解析 dayjs 的源码。
本篇继续解析 dayjs 源码中插件功能的部分,也就是 src/plugin 目录下的文件。挑选出几个代码比较长,实现比较复杂的插件 customFormat、duration、objectSupport、relativeTime、timezone、utc。
在分析源码的过程中也发现了一个规律,dayjs 的文档写的比较不详细,有的插件的用途让人一眼看上去很懵。但是既然 dayjs 实现了 momentjs 的 API,所以当看 dayjs 文档看不懂的时候,就可以去看 momentjs 的中文文档来辅助理解。
目录如下:
- dayjs 源码解析(一):概念、locale、constant、utils
- dayjs 源码解析(二):Dayjs 类
- dayjs 源码解析(三):插件(上)
- dayjs 源码解析(四):插件(中)
- dayjs 源码解析(五):插件(下)
customFormat
customParseFormat 插件扩展了 dayjs 函数对象,使其能支持自定义时间格式。
第一个参数是被解析的字符串,第二个参数是解析用的模板,第三个参数是解析本地化语言的日期字符串或者布尔值或者决定使用严格模式(要求格式和输入内容完全匹配),,返回一个 Dayjs 实例。使用举例:
import dayjs from 'dayjs';
import customParseFormat from 'dayjs/plugin/customParseFormat';
dayjs.extend(customParseFormat);
// 返回一个时间为 '1969-05-02T18:02:03.000Z' 的实例
dayjs('05/02/69 1:02:03 PM -05:00', 'MM/DD/YY H:mm:ss A Z');
// 返回一个时间为 '2018-03-15T00:00:00.000Z' 的实例
dayjs('2018 三月 15', 'YYYY MMMM DD', 'zh-cn');
// 严格解析,分隔符和空格都不能错
dayjs('1970-00-00', 'YYYY-MM-DD', true);
相关知识
| 输入 | 例子 | 详情 | YY | 18 | 两位数的年份 | YYYY | 2018 | 四位数的年份 | M | 1-12 | 月份,从 1 开始 | MM | 01-12 | 月份,两位数 | MMM | Jan-Dec | 缩写的月份名称 | MMMM | January-December | 完整的月份名称 | D | 1-31 | 月份里的一天 | DD | 01-31 | 月份里的一天,两位数 | H | 0-23 | 小时 | HH | 00-23 | 小时,两位数 | h | 1-12 | 小时, 12 小时制 | hh | 01-12 | 小时, 12 小时制, 两位数 | m | 0-59 | 分钟 | mm | 00-59 | 分钟,两位数 | s | 0-59 | 秒 | ss | 00-59 | 秒 两位数 | S | 0-9 | 毫秒,一位数 | SS | 00-99 | 毫秒,两位数 | SSS | 000-999 | 毫秒,三位数 | Z | -05:00 | UTC 的偏移量 | ZZ | -0500 | UTC 的偏移量,两位数 | A | AM PM | 上午 下午 大写 | a | am pm | 上午 下午 小写 | Do | 1st... 31st | 带序数词的月份里的一天 |
|---|
源码分析
插件实现时,最关键的三个方法是 parse、parseFormattedInput 和 makeParser。把三个方法中最核心的部分挑出来:
parse,解析的入口,调用parseFormattedInput。parseFormattedInput,调用makeParser生成对应模板的解析器,解析后返回对应Date对象。makeParser,接收模板,返回解析器。
/**
* @description: 扩展parse方法
* @param {Object} cfg config对象
*/
proto.parse = function (cfg) {
this.$d = parseFormattedInput(date, format, utc);
this.init();
};
/**
* @description: 利用时间字符串和模板来解析出Date对象
* @param {String} input Jan/02/69 1:02:03 PM -05:00
* @param {String} format MMM/DD/YY H:mm:ss A Z
* @param {Boolean} utc 是否为UTC
* @return {Date} 返回对应的时间对象
*/
const parseFormattedInput = (input, format, utc) => {
// 用模板生成解析器
const parser = makeParser(format);
// 解析器去解析时间字符串,生成time对象
const {
year,
month,
day,
hours,
minutes,
seconds,
milliseconds,
zone,
} = parser(input);
return new Date(y, M, d, h, m, s, ms);
};
/**
* @description: 生成一个解析器函数
* @param {String} format 时间模板 举例 MMM/DD/YY H:mm:ss A Z
* @return {Function} 返回新生成的解析器
*/
function makeParser(format) {
const array = format.match(formattingTokens);
for (let i = 0; i < length; i += 1) {
array[i] = { regex, parser };
}
// 到了这一步,array是[{regex, parser}]
/**
* @description: 解析器,输入对应格式时间字符串,返回time对象
* @param {String} input 例如 Jan/02/69 1:02:03 PM -05:00
* @return {Object} 返回time对象
*/
return function (input) {
const time = {};
// 迭代着去匹配替换
for (let i = 0, start = 0; i < length; i += 1) {
const { regex, parser } = array[i];
//...
parser.call(time, value);
input = input.replace(value, '');
}
// 返回时间对象
return time;
};
}
duration
duration 插件用来支持时间跨度。具体的 API 可以参照Moment的 duration。
使用举例:
import duration from 'dayjs/plugin/duration';
dayjs.extend(duration);
// 数字和单位的形式设置时长
dayjs.duration(2, 'minutes');
// 对象形式设置时长
dayjs.duration({
seconds: 2,
minutes: 2,
hours: 2,
days: 2,
weeks: 2,
months: 2,
years: 2,
});
// 加后缀
dayjs.duration(-1, 'minutes').humanize(true); // 1 分钟前
// 提取出毫秒单位的数值
dayjs.duration(1500).milliseconds(); // 500
// 转化为毫秒数返回
dayjs.duration(1500).asMilliseconds(); // 1500
// 返回以秒为基础的长度,保留小数
dayjs.duration(1500).as('seconds'); // 1.5
源码分析
duration 的实现比较复杂,它实际上是实现了一个 Duration类,用它来返回一个 duration实例 后,在实例上处理各种方法。
最后把实例化 Duration类的方法绑定到了 dayjs函数对象 上,实现了 dayjs.duration(arguments) 的 API。
/**
* @description: 判断是否是Duration的实例
* @param {Any} d
* @return {Boolean}
*/
const isDuration = (d) => d instanceof Duration;
let $d;
let $u;
/**
* @description: Duration实例的封装器
* @param {Number|Object|String} input 值
* @param {Dayjs} instance Dayjs实例
* @param {String} unit 单位
* @return {Duration} 返回一个Duration实例
*/
const wrapper = (input, instance, unit) =>
new Duration(input, unit, instance.$l);
/**
* @description: 给单位加上s
* @param {String} unit
* @return {String} 返回units
*/
const prettyUnit = (unit) => `${$u.p(unit)}s`;
class Duration {
constructor(input, unit, locale) {
// 解析出$d和$ms
return this;
}
/**
* @description: 用$d对象计算出毫秒数,添加到$ms属性中
*/
calMilliseconds() {}
/**
* @description: 将毫秒数解析为多少年月日时分秒毫秒,添加到$d属性中
*/
parseFromMilliseconds() {}
/**
* @description: 返回ISO格式的时长字符串
* @return {String}
*/
toISOString() {}
/**
* @description: toJSON和toISOString是相同的
* @return {String}
*/
toJSON() {}
/**
* @description: 将时长格式化
* @param {String} formatStr 模板字符串
* @return {String} 返回格式化后的时长
*/
format(formatStr) {}
/**
* @description: 返回以某个单位为基础的长度,保留小数
* @param {String} unit 单位
* @return {Number}
*/
as(unit) {}
/**
* @description: 返回以某个单位的长度,只保留该单位,且为整数
* @param {String} unit
* @return {Number}
*/
get(unit) {}
/**
* @description: 给时长添加input * unit
* @param {Number|Duration} input 要添加的时长
* @param {String} unit 单位
* @param {Boolean} isSubtract 是否为减
* @return {Duration} 返回新的Duration实例
*/
add(input, unit, isSubtract) {}
/**
* @description: 给时长减少input * unit
* @param {Number|Duration} input 要添加的时长
* @param {String} unit 单位
* @return {Duration} 返回新的Duration实例
*/
subtract(input, unit) {}
/**
* @description: 设置Duration实例的locale
* @param {Object} l locale对象
* @return {Duration} 返回新的Duration实例
*/
locale(l) {}
/**
* @description: 返回一个相同时长的新实例
* @return {Duration}
*/
clone() {}
/**
* @description: 返回显示一段时长,默认没有后缀
* @param {Boolean} withSuffix 是否添加后缀
* @return {String}
*/
humanize(withSuffix) {}
// 下面都是获取对应单位长度的方法,原理相同,as是转化为带小数的值,不带as是只取这一个单位
milliseconds() {}
asMilliseconds() {}
seconds() {}
asSeconds() {}
minutes() {}
asMinutes() {}
hours() {}
asHours() {}
days() {}
asDays() {}
weeks() {}
asWeeks() {}
months() {}
asMonths() {}
years() {}
asYears() {}
}
/**
* @description: plugin
* @param {Object} o option
* @param {Class} c Dayjs类
* @param {Function} d dayjs函数对象
*/
export default (option, Dayjs, dayjs) => {
$d = dayjs;
$u = dayjs().$utils();
/**
* @description: 把duration方法加到了dayjs函数对象上
* @param {Number|Object|String} input 值
* @param {String} unit 单位
* @return {*}
*/
dayjs.duration = function (input, unit) {};
dayjs.isDuration = isDuration;
const oldAdd = Dayjs.prototype.add;
const oldSubtract = Dayjs.prototype.subtract;
/**
* @description: 扩展add方法
* @param {Duration} value 值
* @param {String} unit 单位
*/
Dayjs.prototype.add = function (value, unit) {};
/**
* @description: 扩展subtract方法
* @param {Duration} value 值
* @param {String} unit 单位
*/
Dayjs.prototype.subtract = function (value, unit) {};
};
objectSupport
ObjectSupport 扩展了 dayjs(), dayjs.utc, dayjs().set, dayjs().add, dayjs().subtract 的 API 以支持传入对象参数。
使用举例:
import objectSupport from 'dayjs/plugin/objectSupport';
dayjs.extend(objectSupport);
// dayjs函数直接支持对象参数
dayjs({
year: 2010,
month: 1,
day: 12,
});
// dayjs函数对象上的方法支持对象参数
dayjs.utc({
year: 2010,
month: 1,
day: 12,
});
// 实例上的方法支持对象参数
dayjs().set({ year: 2010, month: 1, day: 12 });
dayjs().add({ M: 1 });
dayjs().subtract({ month: 1 });
源码分析
支持函数对象的这个插件实现的非常标准,基本上所有的方法都是在扩展原有的方法。
比如下述 parse 的实现,先把老版本的 parse 保存成 oldParse,进行对象版本的 parse 处理后再执行 oldParse,保证同时兼容对象和其他格式。
const oldParse = proto.parse;
/**
* @description: 扩展parse,使其解析对象
* @param {Object} cfg config 配置
*/
proto.parse = function (cfg) {
// 给cfg对象添加了date属性
cfg.date = parseDate.bind(this)(cfg);
oldParse.bind(this)(cfg);
};
再比如 parseDate 的实现,$d 不是对象时就走默认的 date 返回,isObject(date) 为 true 时,再执行对对象形式的 date 处理。
/**
* @description: 扩展parseDate,增加对象的处理
* @param {Object} cfg config 配置
* @return {Date} 返回对应的Date对象
*/
const parseDate = (cfg) => {
const { date, utc } = cfg;
const $d = {};
// 是对象时才走下述逻辑
if (isObject(date)) {
if (!Object.keys(date).length) {
return new Date();
}
const now = utc ? dayjs.utc() : dayjs();
// 格式化各个单位的值
Object.keys(date).forEach((k) => {
$d[prettyUnit(k)] = date[k];
});
const d = $d.day || (!$d.year && !($d.month >= 0) ? now.date() : 1);
const y = $d.year || now.year();
const M = $d.month >= 0 ? $d.month : !$d.year && !$d.day ? now.month() : 0; // eslint-disable-line no-nested-ternary,max-len
const h = $d.hour || 0;
const m = $d.minute || 0;
const s = $d.second || 0;
const ms = $d.millisecond || 0;
// 解析为 Date 对象
if (utc) {
return new Date(Date.UTC(y, M, d, h, m, s, ms));
}
return new Date(y, M, d, h, m, s, ms);
}
return date;
};
而对属性修改的几个方法,则是抽出了共同的地方封装成一个 callObject 方法,然后对老版本的方法统一修改以适应对象。
/**
* @description: 定义了一个绑定调用的基础方法
* @param {Function} call 原本的set add和subtract
* @param {Number|Object} argument 数量或数量对象
* @param {String} string argument 不是对象时需要指定单位 unit
* @param {Number} offset 1是加,-1是减
* @return {*}
*/
const callObject = function (call, argument, string, offset = 1) {
// argument为对象时迭代着修改每个单位
if (argument instanceof Object) {
const keys = Object.keys(argument);
let chain = this;
keys.forEach((key) => {
// 每次返回新实例后要重新绑定this为新实例,所以能迭代的修改各个单位
chain = call.bind(chain)(argument[key] * offset, key);
});
return chain;
}
// argument为Number时,就只修改string单位的值,为了add和subtract用
return call.bind(this)(argument * offset, string);
};
调用的时候如下扩展的 add 方法所示:
/**
* @description: 扩展add
* @param {Number} number 值
* @param {String} string 单位
* @return {Dayjs}
*/
proto.add = function (number, string) {
return callObject.bind(this)(oldAdd, number, string);
};
relativeTime
relativeTime 插件增加了 .from、 .to、 .fromNow、 .toNow 4 个 API 来展示相对的时间 (e.g. 3 小时以前)。
使用示例:
import relativeTime from 'dayjs/plugin/relativeTime';
dayjs.extend(relativeTime);
// 765985205000 === 1994-04-10
dayjs(765985205000).from(dayjs('1990-01-01')); // 4 年内
dayjs(765985205000).fromNow(); // 27 年前
dayjs(765985205000).to(dayjs('1990-01-01')); // 4 年前
dayjs(765985205000).toNow(); // 27 年内
dayjs(765985205000).from(dayjs('1990-01-01'), true); // 4 年
相关知识
范围对应的输出值如下表所示,也可以在插件的 option 中配置 thresholds 进行自定义。
| 范围 | 键值 | 示例输出 | 0 到 44 秒 | s | 几秒前 | 45 到 89 秒 | m | 1 分钟前 | 90 秒 到 44 分 | mm | 2 分钟前 ... 44 分钟前 | 45 到 89 分 | h | 1 小时前 | 90 分 到 21 小时 | hh | 2 小时前 ... 21 小时前 | 22 到 35 小时 | d | 1 天前 | 36 小时 到 25 天 | dd | 2 天前 ... 25 天前 | 26 到 45 天 | M | 1 个月前 | 46 天 到 10 月 | MM | 2 个月前 ... 10 个月前 | 11 月 到 17 月 | y | 1 年前 | 18 月以上 | yy | 2 年前 ... 20 年前 |
|---|
源码分析
四个新添加的相对时间的 API 都是依赖的核心方法 fromTo。
const fromTo = (input, withoutSuffix, instance, isFrom) => {
const loc = instance.$locale().relativeTime || relObj;
// 阈值设置
const T = o.thresholds || [
// 超过44s后被认为是1分钟
{ l: 's', r: 44, d: C.S },
{ l: 'm', r: 89 },
// 超过44分钟后被认为是1小时
{ l: 'mm', r: 44, d: C.MIN },
{ l: 'h', r: 89 },
// 超过21小时后被认为是1天
{ l: 'hh', r: 21, d: C.H },
{ l: 'd', r: 35 },
// 超过25天后被认为是1月
{ l: 'dd', r: 25, d: C.D },
{ l: 'M', r: 45 },
// 超过10个月后被认为是1年
{ l: 'MM', r: 10, d: C.M },
{ l: 'y', r: 17 },
{ l: 'yy', d: C.Y },
];
const Tl = T.length;
let result;
let out;
let isFuture;
// 迭代
for (let i = 0; i < Tl; i += 1) {
let t = T[i];
// 先计算各个单位上的时间差
if (t.d) {
result = isFrom
? d(input).diff(instance, t.d, true)
: instance.diff(input, t.d, true);
}
const abs = (o.rounding || Math.round)(Math.abs(result));
// 判断是过去还是未来
isFuture = result > 0;
if (abs <= t.r || !t.r) {
// 找到要转换的单位,开始格式化
if (abs <= 1 && i > 0) t = T[i - 1]; // 1 minutes -> a minute, 0 seconds -> 0 second
const format = loc[t.l];
if (typeof format === 'string') {
out = format.replace('%d', abs);
} else {
out = format(abs, withoutSuffix, t.l, isFuture);
}
break;
}
}
// 不需要后缀就直接返回
if (withoutSuffix) return out;
/**
* @description: 添加后缀的函数
* @param {Boolean} isFuture 是未来还是过去
* @return {String} 返回需要添加的后缀
*/
const pastOrFuture = isFuture ? loc.future : loc.past;
if (typeof pastOrFuture === 'function') {
return pastOrFuture(out);
}
// 需要后缀就添加后缀
return pastOrFuture.replace('%s', out);
};
timezone
Timezone 插件添加了 dayjs.tz、 .tz、 .tz.guess、 .tz.setDefault 的 API,在时区之间解析或显示。
使用示例:
import timezone from 'dayjs/plugin/timezone';
import utc from 'dayjs/plugin/utc';
dayjs.extend(timezone);
dayjs.extend(utc);
// 返回一个设置好时区和时刻的新的Dayjs实例
dayjs.tz('2014-06-01 12:00', 'America/New_York');
// 将实例设置时区,并返回新实例
dayjs('2014-06-01 12:00').tz('America/New_York');
// 返回时区标志字符串
dayjs.tz.guess();
// 设置默认时区标志字符串
dayjs.tz.setDefault('America/New_York');
相关知识
时区
要理解时区,先看下图,我们在本系列第一节的基本概念中讲到过,格林尼治平均时间(Greenwich Mean Time,GMT)是指位于英国伦敦郊区的皇家格林尼治天文台当地的平太阳时。
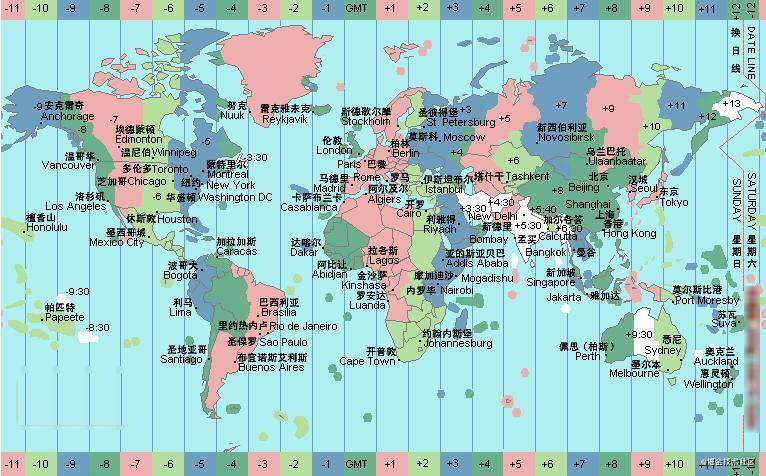
全球 360° ,每 15° 划分一个理论时区,总共 24 个,理论时区以被 15 整除的经线为中心,向东西两侧延伸 7.5 度,即每 15° 划分一个时区。理论时区的时间采用其中央经线(或标准经线)的地方时。所以每差一个时区,区时相差一个小时,相差多少个时区,就相差多少个小时。另外,为了避开国界线,有的时区的形状并不规则,而且比较大的国家以国家内部行政分界线为时区界线,这是实际时区,即法定时区,可见上图。
协调世界时
如果时间是以协调世界时(UTC)表示,则在时间后面直接加上一个“Z”(不加空格)。“Z”是协调世界时中 0 时区的标志。因此,“09:30 UTC”就写作“09:30Z”或是“0930Z”。“14:45:15 UTC”则为“14:45:15Z”或“144515Z”。
UTC 时间也被叫做祖鲁时间,因为在北约音标字母中用“Zulu”表示“Z”。
UTC 偏移量
UTC 偏移量用以下形式表示:±[hh]:[mm]、±[hh][mm]、或者 ±[hh]。如果所在区时比协调世界时早 1 个小时(例如柏林冬季时间),那么时区标识应为“+01:00”、“+0100”或者直接写作“+01”。这也同上面的“Z”一样直接加在时间后面。
"UTC+8"表示当协调世界时(UTC)时间为凌晨 2 点的时候,当地的时间为 2+8 点,即早上 10 点。
缩写
时区通常都用字母缩写形式来表示,例如“EST、WST、CST”等。但是它们并不是 ISO 8601 标准的一部分,不应单独用它们作为时区的标识。
源码分析
这里的代码实现的比较复杂而且难以理解,主要原因是为了计算准确的 UTC 偏移量进行 bugfix,加入了 Intl 的 API。
// 从 Intl.DateTimeFormat中 缓存检索的时区,因为这个方法非常慢。
const dtfCache = {};
/**
* @description: 获取Intl.DateTimeFormat格式化后的时间
* @param {String} timezone 时区字符串 例如 America/New_York
* @param {Object} options 选项
* @return {DateTimeFormat} 返回对应时区DateTimeFormat实例,主要是利用实例上的format方法
*/
const getDateTimeFormat = (timezone, options = {}) => {
// 时区名称的展现方式,默认为short
const timeZoneName = options.timeZoneName || 'short';
const key = `${timezone}|${timeZoneName}`;
// 优先从缓存中拿
let dtf = dtfCache[key];
if (!dtf) {
dtf = new Intl.DateTimeFormat('en-US', {
hour12: false,
timeZone: timezone,
year: 'numeric',
month: '2-digit',
day: '2-digit',
hour: '2-digit',
minute: '2-digit',
second: '2-digit',
timeZoneName,
});
dtfCache[key] = dtf;
}
return dtf;
};
最核心的方法是 tz 方法,这个方法返回一个设置好 UTC 偏移量的新的 Dayjs实例。实现时主要就是根据时差对 Dayjs实例 进行了各种修正。
/**
* @description: 返回一个设置好UTC偏移量的新的Dayjs实例
* @param {String} timezone 时区标志 America/New_York
* @param {Boolean} keepLocalTime 是否保持Local的偏移
* @return {Dayjs} 返回一个设置好UTC偏移量的新的Dayjs实例
*/
proto.tz = function (timezone = defaultTimezone, keepLocalTime) {
const oldOffset = this.utcOffset();
// 利用原生的Date对象
const target = this.toDate().toLocaleString('en-US', { timeZone: timezone });
const diff = Math.round((this.toDate() - new Date(target)) / 1000 / 60);
// 给实例设置UTC偏移量
let ins = d(target)
.$set(MS, this.$ms)
.utcOffset(localUtcOffset - diff, true);
// 如果需要保持本地时间,就再修正偏移
if (keepLocalTime) {
const newOffset = ins.utcOffset();
ins = ins.add(oldOffset - newOffset, MIN);
}
ins.$x.$timezone = timezone;
return ins;
};
utc
Day.js 默认使用用户本地时区来解析和展示时间。 如果想要使用 UTC 模式来解析和展示时间,可以使用 dayjs.utc() 而不是 dayjs()。
使用示例:
import utc from 'dayjs/plugin/utc';
dayjs.extend(utc);
// 默认当地时间
dayjs().format(); //2019-03-06T17:11:55+08:00
// UTC 模式
dayjs.utc().format(); // 2019-03-06T09:11:55Z
// 将本地时间转换成 UTC 时间
dayjs().utc().format(); // 2019-03-06T09:11:55Z
// 在 UTC 模式下,所有的展示方法都将使用 UTC 而不是本地时区
// 所有的 get 和 set 方法也都会使用 Date#getUTC* 和 Date#setUTC* 而不是 Date#get* and Date#set*
dayjs.utc().isUTC(); // true
dayjs.utc().local().format(); //2019-03-06T17:11:55+08:00
dayjs.utc('2018-01-01', 'YYYY-MM-DD'); // with CustomParseFormat plugin
源码分析
代码中区分 UTC 模式和本地模式的标志就是 config 配置对象中的 utc 属性。如下述代码所示,不管是 dayjs 函数对象还是实例上的 utc 方法,都是用 utc: true 来进行区分。
/**
* @description: 返回一个新的包含 UTC 模式标记的 Dayjs 实例。
* @param {Date} date Date对象
* @return {Dayjs} 返回一个Dayjs实例
*/
dayjs.utc = function (date) {
// 关键在于utc: true
const cfg = { date, utc: true, args: arguments };
return new Dayjs(cfg);
};
/**
* @description: 返回一个新的包含 UTC 模式标记的 Dayjs 实例。
* @param {Boolean} keepLocalTime 是否保持本地时间
* @return {Dayjs} 返回一个Dayjs实例
*/
proto.utc = function (keepLocalTime) {
const ins = dayjs(this.toDate(), { locale: this.$L, utc: true });
if (keepLocalTime) {
return ins.add(this.utcOffset(), MIN);
}
return ins;
};
同样的原理,如果实例要启用本地时间,将 utc: false 即可。
/**
* @description: 返回一个复制的包含使用本地时区标记的 Dayjs 对象。
* @return {Dayjs} 返回一个Dayjs实例
*/
proto.local = function () {
// 关键是utc为false
return dayjs(this.toDate(), { locale: this.$L, utc: false });
};
对于其他方法的扩展,基本上都是修正本地时间与 UTC 时间的偏移后再调用 oldProto 上的同名方法,不再赘述。
本篇内容完成,下一篇中将继续分析剩余的简单插件。
前端记事本,不定期更新,欢迎关注!
- 微信公众号: 林景宜的记事本
- 博客:林景宜的记事本
- 掘金专栏:林景宜的记事本
- 知乎专栏: 林景宜的记事本
- Github: MageeLin
常见问题FAQ
- 免费下载或者VIP会员专享资源能否直接商用?
- 本站所有资源版权均属于原作者所有,这里所提供资源均只能用于参考学习用,请勿直接商用。若由于商用引起版权纠纷,一切责任均由使用者承担。更多说明请参考 VIP介绍。
- 提示下载完但解压或打开不了?
- 找不到素材资源介绍文章里的示例图片?
- 模板不会安装或需要功能定制以及二次开发?




发表评论
还没有评论,快来抢沙发吧!